TrofyBot: A Transformable Rolling and Flying Robot with High Energy Efficiency
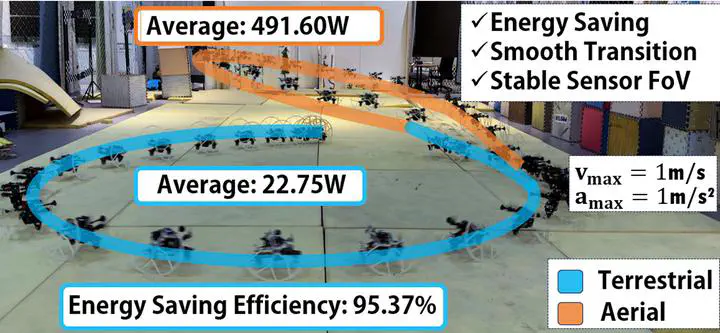 Image credit: FAST-FIRE
Image credit: FAST-FIREAbstract
Terrestrial and aerial bimodal vehicles have gained significant interest due to their energy efficiency and versatile maneuverability across different domains. However, most existing passive-wheeled bimodal vehicles rely on attitude regulation to generate forward thrust, which inevitably results in energy waste on producing lifting force. In this work, we propose a novel passive-wheeled bimodal vehicle called TrofyBot that can rapidly change the thrust direction with a single servo motor and a transformable parallelogram linkage mechanism (TPLM). Cooperating with a bidirectional force generation module (BFGM) for motors to produce bidirectional thrust, the robot achieves flexible mobility as a differential driven rover on the ground. This design achieves 95.37% energy saving efficiency in terrestrial locomotion, allowing the robot continuously move on the ground for more than two hours in current setup. Furthermore, the design obviates the need for attitude regulation and therefore provides a stable sensor field of view (FoV). We model the bimodal dynamics for the system, analyze its differential flatness property, and design a controller based on hybrid model predictive control for trajectory tracking. A prototype is built and extensive experiments are conducted to verify the design and the proposed controller, which achieves high energy efficiency and seamless transition between modes.